The Cottrell Experiment and Diffusion Limitation 3/3
$ 13.00 · 4.7 (315) · In stock
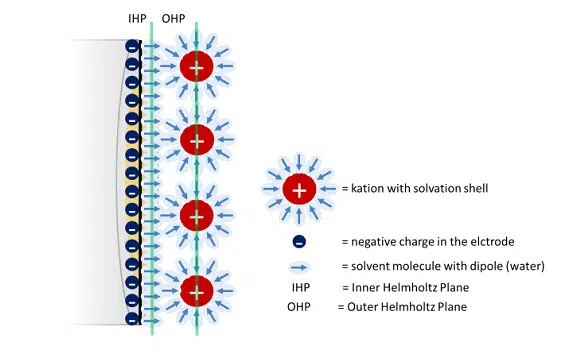
In this chapter the electrochemical double layer and its features are discussed. The electrochemical double layer acts as a capacitor and every change in the potential of the electrode will induce a capacitive charging current that is caused by physics not by a chemical reaction. This current decays exponentially.
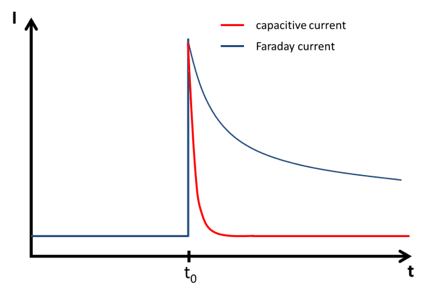
Capacitive Current - PalmSens

Fluorinated ether decomposition in localized high concentration electrolytes - ScienceDirect

PDF) Comparison between Cottrell diffusion and moving boundary models for determination of the chemical diffusion coefficients in ion-insertion electrodes

Fabrication of Ag@Co-Al Layered Double Hydroxides Reinforced poly(o-phenylenediamine) Nanohybrid for Efficient Electrochemical Detection of 4-Nitrophenol, 2,4-Dinitrophenol and Uric acid at Nano Molar Level

How to optimize the analytical performance of differential pulse voltammetry: one variable at time versus Design of Experiments
PDF) Comparison between Cottrell diffusion and moving boundary models for determination of the chemical diffusion coefficients in ion-insertion electrodes
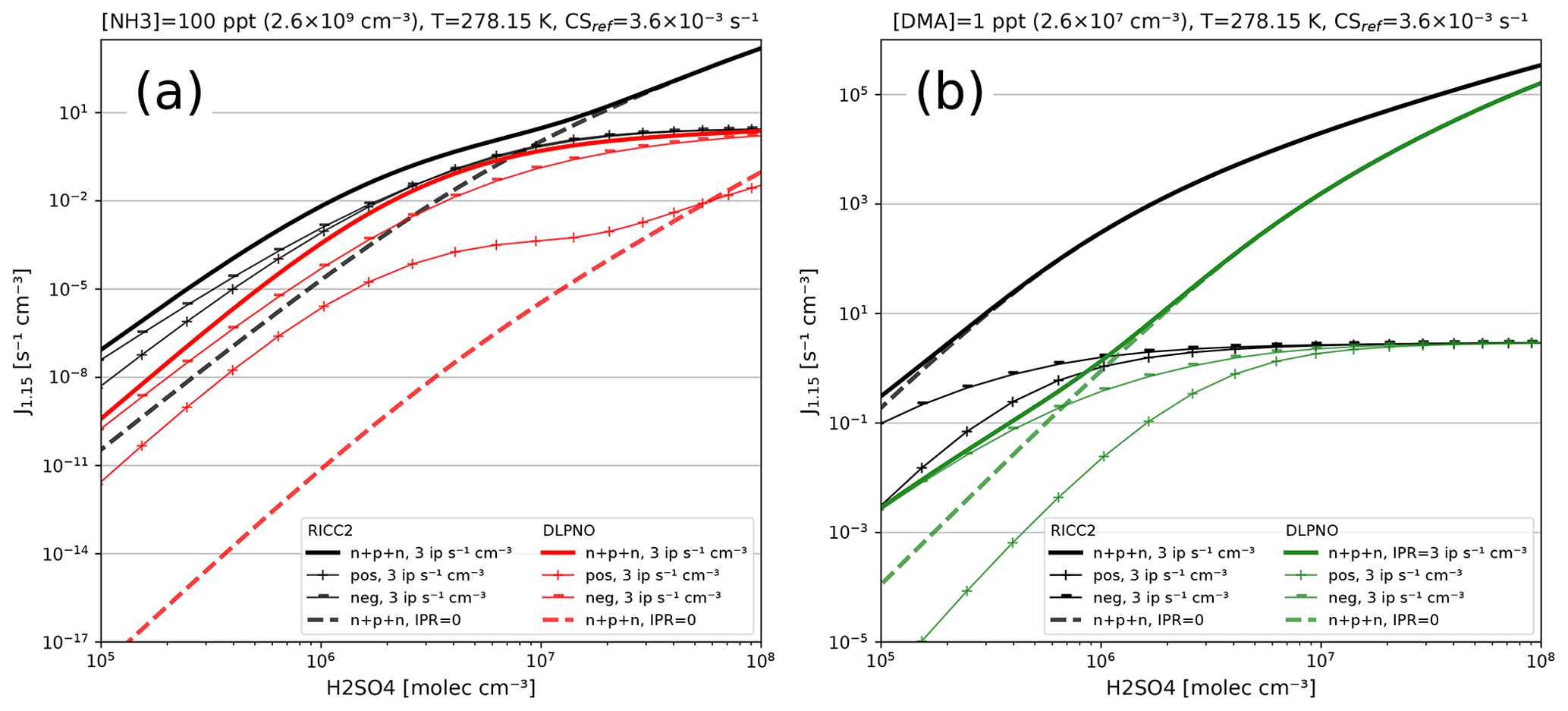
GMD - Atmospherically Relevant Chemistry and Aerosol box model – ARCA box (version 1.2)

The Cottrell Experiment and Diffusion Limitation 2/3 - The Cottrell Experiment - PalmSens
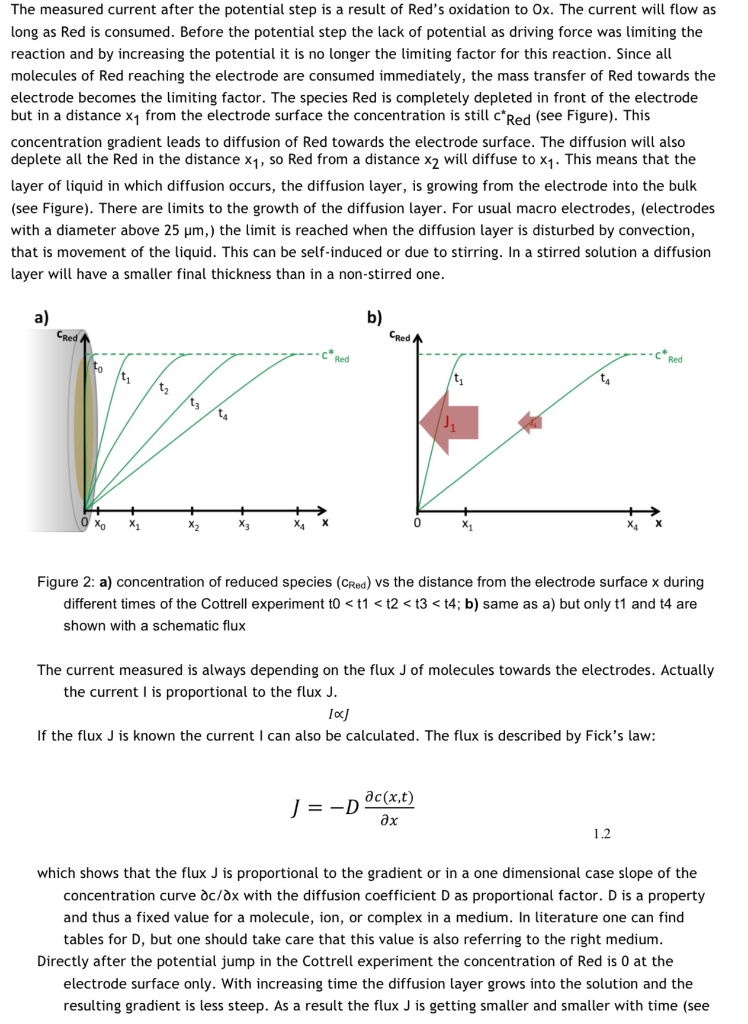
Figure 1.1: Cottrell experiment in KCl solution with

The interpretation of small molecule diffusion coefficients: Quantitative use of diffusion-ordered NMR spectroscopy - ScienceDirect

Electrochemistry with Stationary Disk and Ring−Disk Millielectrodes in Magnetic Fields

Polymers, Free Full-Text

Localized or Spatially Selective Electrodeposition Methods