Physiology of the Pineal Gland and Melatonin - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf
$ 21.50 · 4.7 (708) · In stock

The pineal gland was described as the “Seat of the Soul” by Renee Descartes and it is located in the center of the brain. The main function of the pineal gland is to receive information about the state of the light-dark cycle from the environment and convey this information by the production and secretion of the hormone melatonin. Changing photoperiod is indicated by the duration of melatonin secretion and is used by photoperiodic species to time their seasonal physiology. The rhythmic production of melatonin, normally secreted only during the dark period of the day, is extensively used as a marker of the phase of the internal circadian clock. Melatonin itself is used as a therapy for certain sleep disorders related to circadian rhythm abnormalities such as delayed sleep phase syndrome, non-24h sleep wake disorder and jet lag. It might have more extensive therapeutic applications in the future, since multiple physiological roles have been attributed to melatonin. It exerts physiologic immediate effects during night or darkness and when suitably administered has prospective effects during daytime when melatonin levels are undetectable. In addition to its role in regulating seasonal physiology and influencing the circadian system and sleep patterns, melatonin is involved in cell protection, neuroprotection, and the reproductive system, among other possible functions. Pineal gland function and melatonin secretion can be impaired due to accidental and developmental conditions, such as pineal tumors, craniopharyngiomas, injuries affecting the sympathetic innervation of the pineal gland, and rare congenital disorders that alter melatonin secretion. This chapter summarizes the physiology and pathophysiology of the pineal gland and melatonin. For complete coverage of all related areas of Endocrinology, please visit our on-line FREE web-text, WWW.ENDOTEXT.ORG.
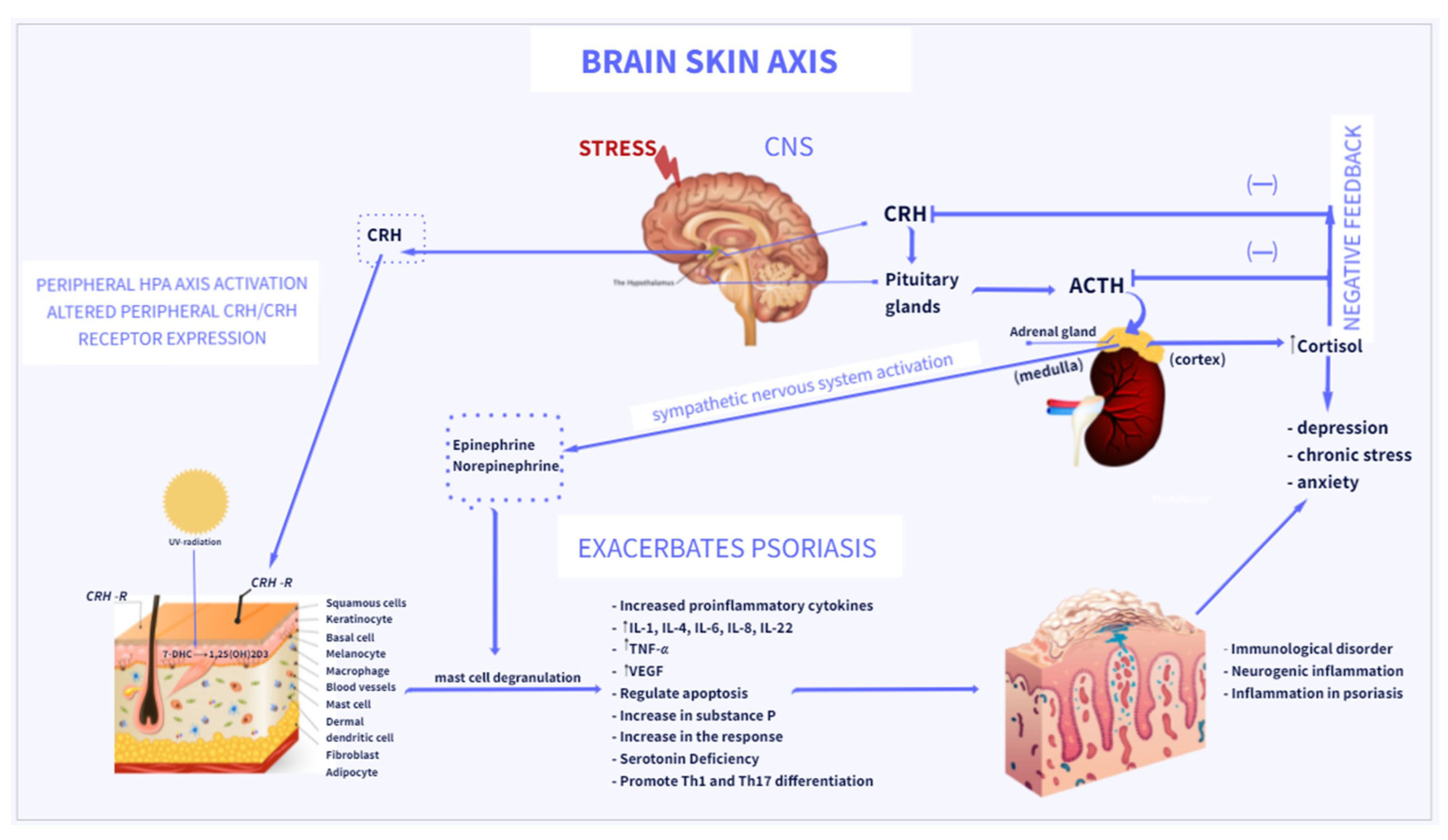
IJMS, Free Full-Text
Functia Integrativa A Creierului PDF, PDF, Circadian Rhythm
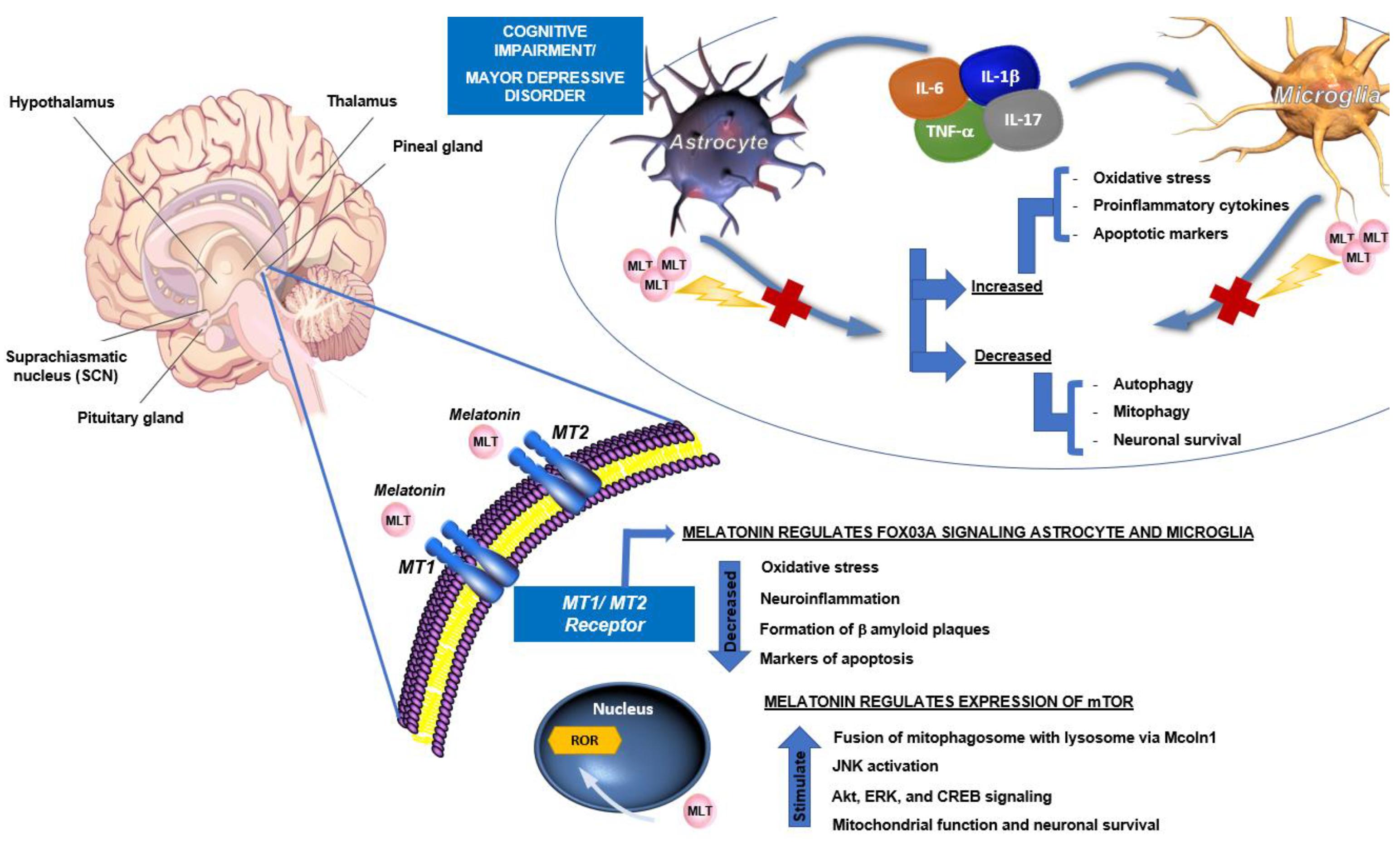
Molecules, Free Full-Text

Pineal Gland: What Is It, Where Is It, Its Function and More
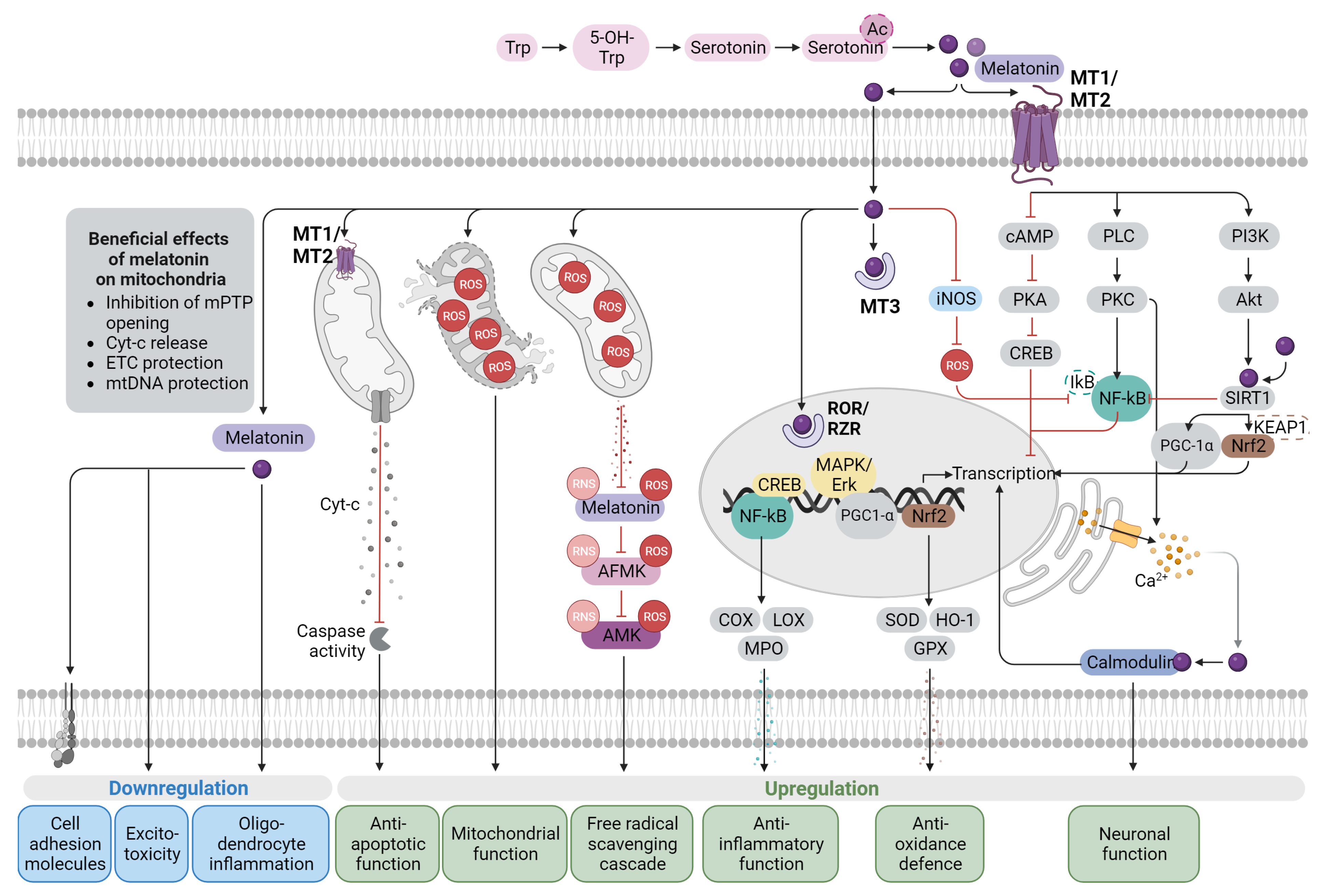
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text

PDF] Stress, Endocrine Physiology and Pathophysiology - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf

Benefits And Uses Of Vitamin E Capsules How To Use Evion, 50% OFF

Physiology of the Pineal Gland and Melatonin - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf

Functional Anatomy of the Hypothalamus and Pituitary - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf
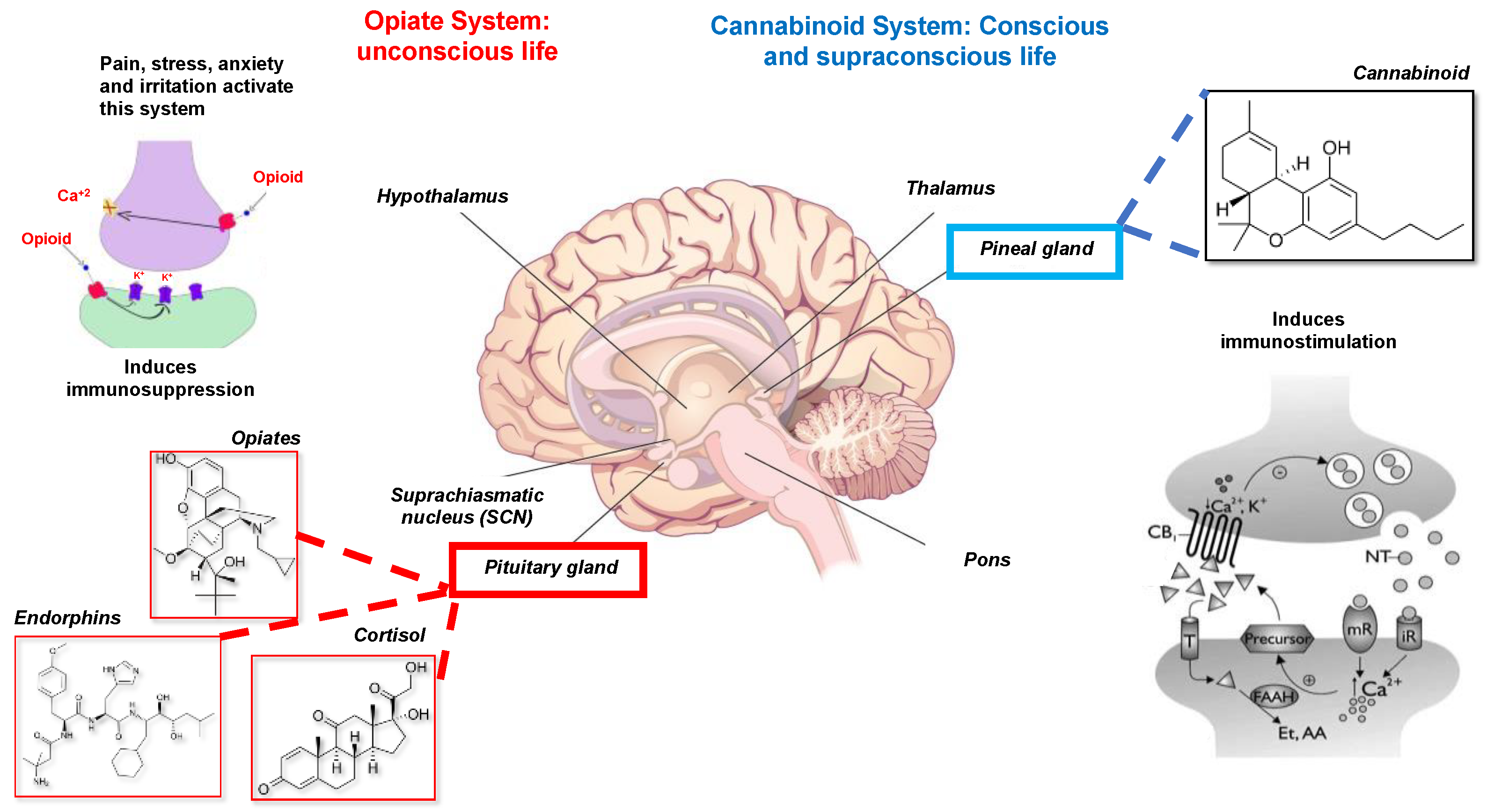
Molecules, Free Full-Text
Irwan, S.Si: Program Pasca Sarjana Program Studi Kimia Universitas Halu Oleo 2017

