Fluids, Free Full-Text
$ 6.50 · 4.6 (724) · In stock
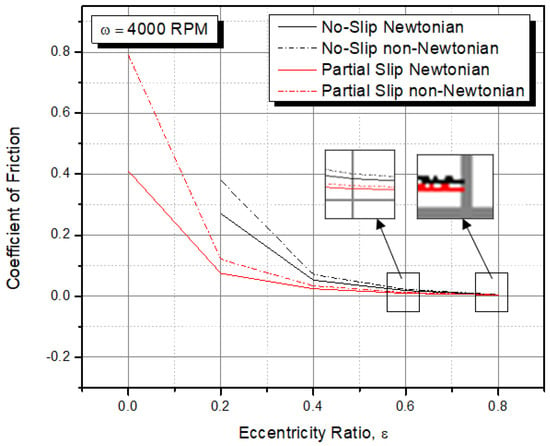
It is a well-known fact that incorporating a slip boundary into the contact surfaces improves bearing performance significantly. Regrettably, no research into the effect of slip on the behavior of journal bearing systems operating with non-Newtonian lubricants has been conducted thus far. The main purpose of this work is to explore the performance comparison of Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluid on a heterogeneous slip/no-slip journal bearing system. The tribological and acoustic behavior of journal bearing is investigated in this study using a rigorous program that combines CFD (computational fluid dynamics) and two-way FSI (fluid–structure interaction) procedures to simulate Newtonian vs. non-Newtonian conditions with and without slip boundary. The numerical results indicate that irrespective of the lubricant type (i.e., Newtonian or non-Newtonian), an engineered heterogeneous slip/no-slip pattern leads to the improvement of the bearing performance (i.e., increased load-carrying capacity, reduced coefficient of friction, and decreased noise) compared to conventional journal bearing. Furthermore, the influence of the eccentricity ratio is discussed, which confirms that the slip beneficial effect becomes stronger as the eccentricity ratio decreases. It has also been noticed that the Newtonian lubricant is preferable for improving tribological performance, whereas non-Newtonian fluid is recommended for lowering bearing noise.

IV Fluids and Solutions Guide & Cheat Sheet (2023 Update) - Nurseslabs
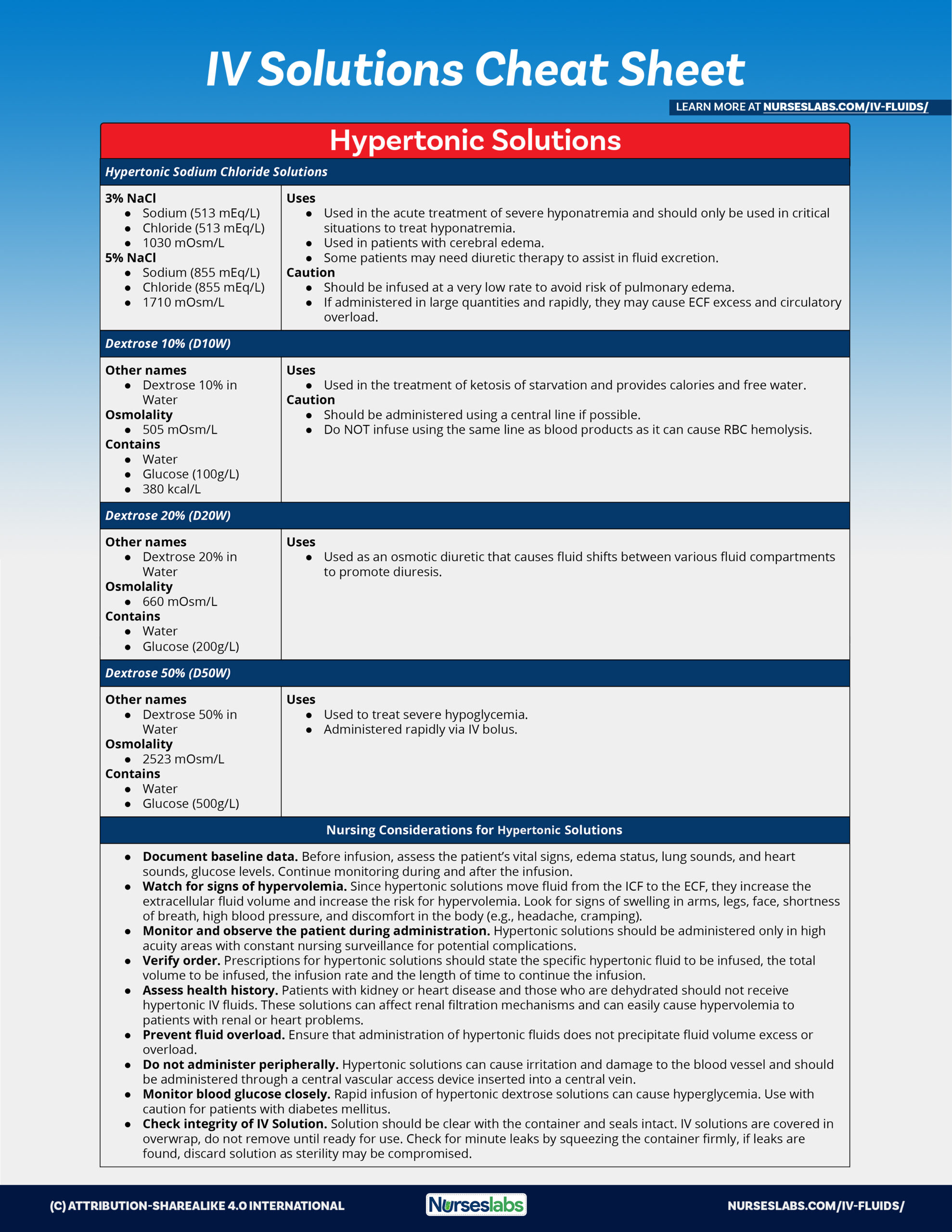
IV Fluids and Solutions Guide & Cheat Sheet (2023 Update) - Nurseslabs
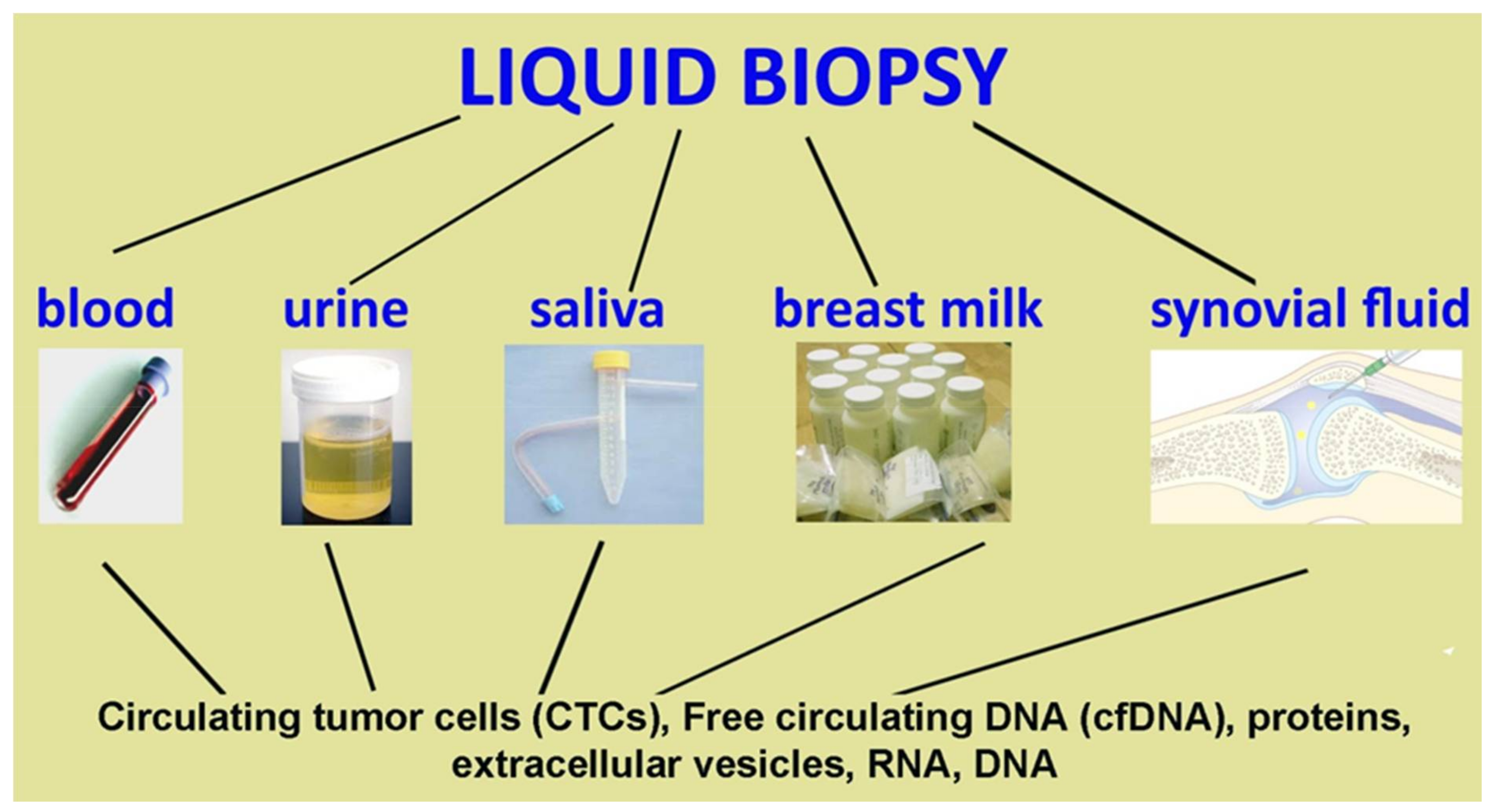
Diagnostics, Free Full-Text
State lawmakers consider lifting raw milk restrictions to include humans - Georgia Recorder, Raw Milk

Fluids, Free Full-Text

Fluid mechanics, Definition, Equations, Types, & Facts

Comparison of Two Fluid-Management Strategies in Acute Lung Injury

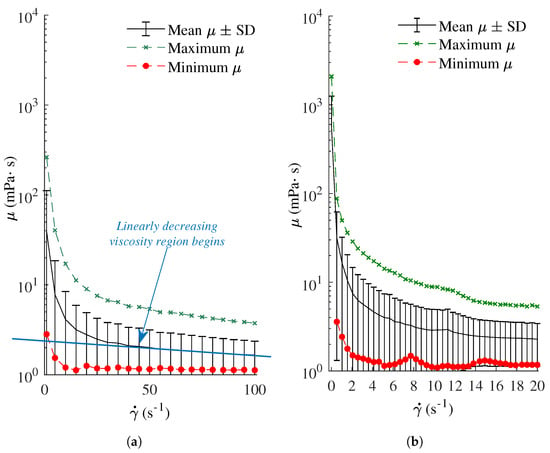
Fluids, Free Full-Text
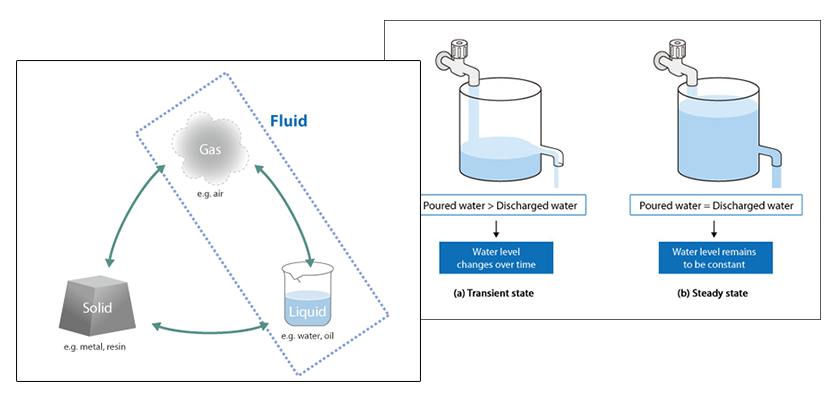
Basic Course of Thermo-Fluid Analysis 06: Chapter 3 Basics of Flow - 3.2.1 Compressible/incompressible fluids|List