ESTROGENS AND ANDROGENS - ppt download
$ 9.50 · 4.9 (152) · In stock

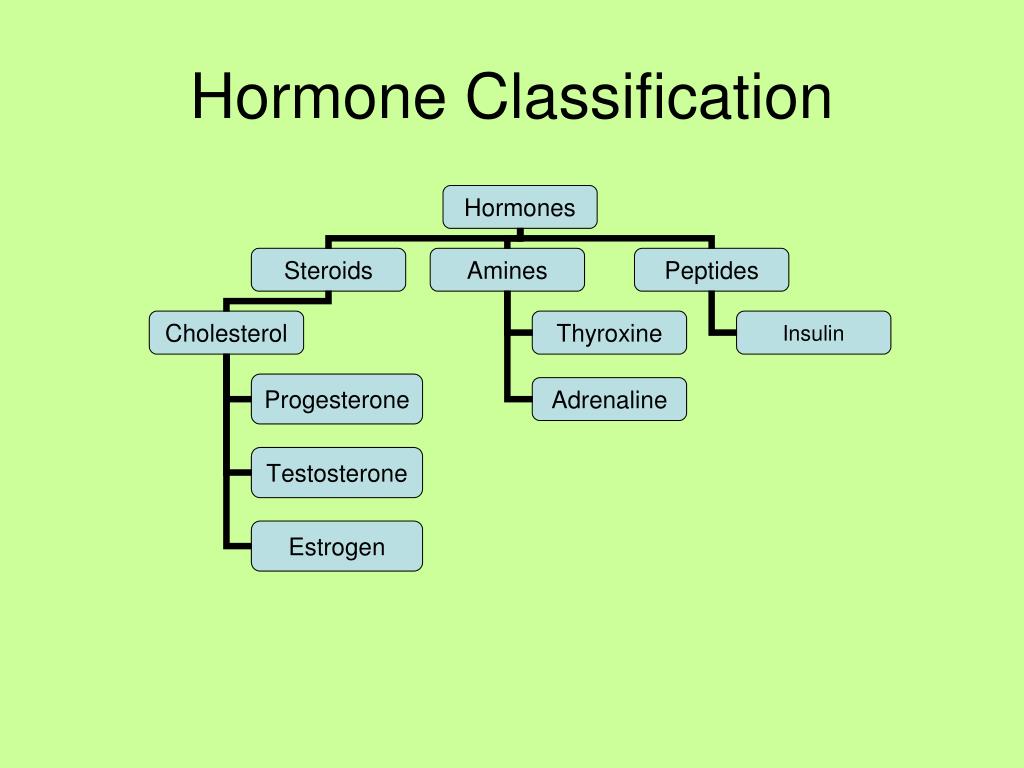
Estrogens Natural: Estradiol, estrone & estriol Conjugated: premarin (estrone and equillin) Steroidal synthetic: Mestranol & Ethinyl estradiol Non-steroidal synthetic: Diethylstilbesterol Rationale for synthetic: to ↑ oral-bioavailability, half-life and ↑ feedback inhibition on FSH & LH
Conjugated: premarin (estrone and equillin) Steroidal synthetic: Mestranol & Ethinyl estradiol. Non-steroidal synthetic: Diethylstilbesterol. Rationale for synthetic: to ↑ oral-bioavailability, half-life and ↑ feedback inhibition on FSH & LH.
Oral – Premarin ( Estrone + Equilin) , Estinyl estradiol , Mestranol. Excretion - Renal.
Contraception: ↓ feedback release of gonadotropins. Female Hypogonadism (estrogen + progestin) or ovarian failure. Estrogens for hormone replacement therapy in menopausal women to ↓ bone resorption. Uterine bleeding. Dysmenorrhea. Men with androgen dependent prostate cancer to slow the growth of the cancer cell.
SIDE EFFECT: Nausea. Breast tenderness. Endometrial hyperplasia. Increased skin pigmentation. Increased blood coagulation at high doses. Increased risk of endometrial cancer unless progestin is added. Breakthrough bleeding. DES clear cell adenocarcinoma of vagina in females exposed to DES in utero. Estrogen increases melanin. Increase factor 2, 7, 9 & 10 as well as decrease antithrombin III.
With estrogen-dependent neoplasm (e.g. endometrial carcinoma) At higher risk for or with breast carcinoma that are estrogen dependent. Predisposed to thromboembolic disease.
Are non-steroidal compounds that bind to estrogen receptors. They can act as either agonist, partial agonists and antagonists depending on the tissue.
Breast: antagonist. Endometrium: a partial agonist with the risk of increasing endometrial cancer. USES: estrogen dependent breast cancer. SE: Hot flushes, nausea and vomiting.
USES: prophylaxis of postmenopausal osteoporosis. SE: increased risk of DVT, pulmonary embolism.
USE: for infertility caused by anovulatory cycle such as those seen in patients with PCOS. Side effect: multiple pregnancies, ovarian enlargement.
MOA: is an aromatase inhibitor, resulting in decreased estrogen synthesis. USE: estrogen-dependent postmenopausal breast cancer.
Progesterone: major natural progesterone. Medroxyprogesterone. Norethindrone. 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone. Norgestrel. Desogestrel: devoid of androgenic and antiestrogenic actions.
Major uses: hormone contraception : ↑ feedback inhibition esp LH → no ovulation. hormone replacement treatment along with estrogen to decrease endometrial cancer. dysmenorrhea.
reduce plasma HDL ↑LDL. Breakthrough bleeding. Acne, weight gain and hirsutism (androgenic effect)
Used as an abortifacient, administered with misoprostol (PGE₁) Also an antiglucocorticoid. SIDE EFFECT: bleeding, GI effects(nausea, vomiting) and abdominal pain.
Progestins (Mini pill) only (norethindrone or norgestrel) Estrogens and progestins (combination pills) Progestin implants. Post-coital contraception uses estrogen (mestranol or etinyl estradiol) Mechanism of Action: contraception. ovulation-inhibition by suppressing gonadotropins. change in cervical mucus(progesterone)
Can result in unwanted pregnancies.
ADVANTAGE. DISADVANTAGE. Reliable (<1% failure) Taken daily. ↓ risk of endometrial and ovarian cancer. No protection against STDs. ↓ pelvic infections. ↑ triglycerides. ↓ risk of osteoporosis. Depression, weight gain, nausea, hypertension. No dysmenorrhea. Hypercoagulable state.
Increase skin pigmentation. Weight gain. Breakthrough bleeding. Withdrawal bleeding.
PROGESTIN: Weight gain Hirsutism Acne Increase LDL
Venous Thromboembolic Disease. breakthrough bleeding. Withdrawal bleeding. RISK FACTORS: Smoking, Increased age.
dihydrotestosterone. Fluoxymesterone. Danazol. androstenedione. Nandrolone.
USES: Male hypogonadism For anabolic actions to increase muscle mass Illicit use in athletes
Acne. excessive libido & erections, increased muscle & bone mass, aggravation of pre existing prostate cancer. Reduce plasma HDL and increase LDL.
Danazol. used in the treatment of endometriosis which is the growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, especially in the pelvis.
SE: Excessive masculinization. Premature closure of epiphysis. Aggression. Dependence and abuse. Depression of menses and hirsutism in women.
Pregnant women: its teratogenic. Children Androgens - Not used in children. Men with prostatic carcinoma.
Anti-Androgen Cyproterone acetate Flutamide Finasteride
Symptomatic Management of prostatic carcinoma. Management of BPH.
Conversion Inhibitors. Finasteride: Inhibits 5 alpha reductase. decreases dihydrotestosterone levels in the prostate. Uses – BPH to reduce the size of the prostate and male pattern baldness. Has been replaced by α1 blockers in the symptomatic treatment of BPH. DHT causes hair loss and prostate enlargement.
Cyproterone & Cyproterone acetate. Clinical use: Women - hirsutism. Men - reduction of sexual drive.
Used in androgen receptor positive Prostatic Carcinoma. Testosterone causes the cancer cell to grow more rapidly.
Bicalutamide Effective orally for the treatment of metastatic prostatic cancer.

Supplementation with flaxseed alters estrogen metabolism in postmenopausal women to a greater extent than does supplementation with an equal amount of soy123 - The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
PPT - Hormones PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:545054
Free Hormone Glands Enzymes Medical PowerPoint Template for Medical PowerPoint Presentations

Foxa1 and Foxa2 Are Essential for Sexual Dimorphism in Liver Cancer: Cell

CYP19A1 mediates severe SARS-CoV-2 disease outcome in males - ScienceDirect

ESTROGENS AND ANDROGENS - ppt download

Effects of phytoestrogens on reproductive organ health

PPT - Estrogens & Antiestrogens PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:3881057

Hormones Released from the Anterior Pituitary or Adenohypophysis Somatotrophs Human Growth Hormone (hGH) Hypothalam…